Digital transformation of Switzerland’s healthcare system: The obstacles
Medicine is facing a digital transformation. In Switzerland, however, various obstacles make it difficult for healthcare stakeholders to shape future digital health in a responsible way.
In an intensive dialogue, the research team around ETH professor Effy Vayena talked to healthcare stakeholders about the main obstacles hindering the responsible implementation of digital healthcare. The interviews proved to be “unexpectedly successful” in that 46 high-ranking representatives of the key interest groups were willing to share their views. About 100 digital meetings, moderated discussions and individual re-clustering ultimately resulted in a web-based mind map of the principal barriers to a responsible implementation of digital healthcare provision in Switzerland.
Core impediments to digital health
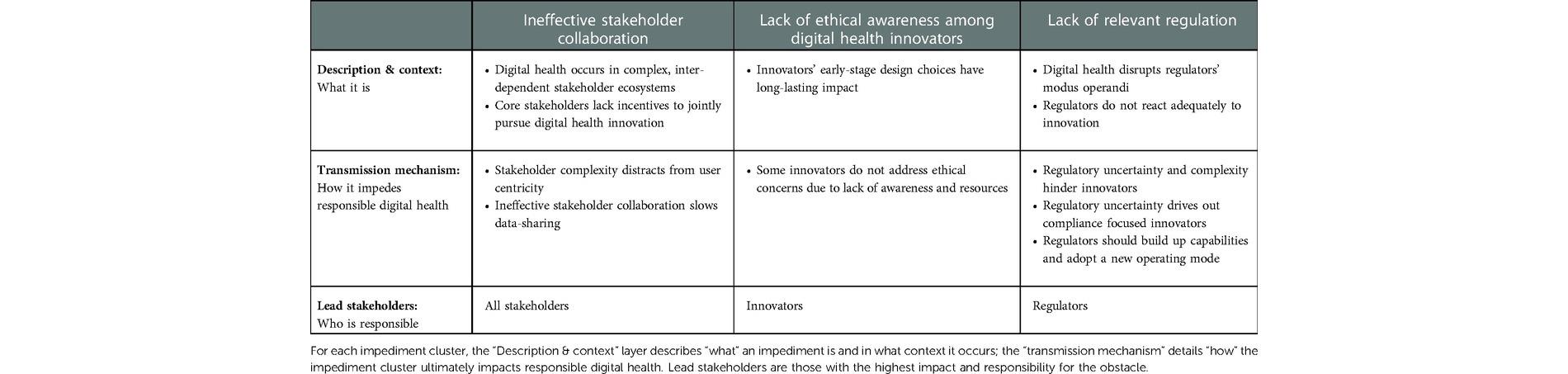
Vayena and her team sorted the main impediments obstructing responsible digital health into three groups:
- ineffective cooperation of stakeholders
- lack of ethical awareness among innovators in the field of digital health
- absence of standards and guidelines
Reason 1: Inefficient cooperation among interest groups
Digital health involves complex and interdependent stakeholder networks. The actors that have entered the relevant sectors recently, which include both start-ups and major technology companies such as Amazon and Microsoft, are adding further to the complexity of this ecosystem. Cooperation in this environment is inefficient. Moreover, the lack of uniform standards or central platforms is impeding cooperation.
Participants stress that for certain core stakeholders there are not enough incentives for supporting and carrying through with responsible digital health.
Reason 2: Digital health innovators often lack ethical awareness
The stakeholders interviewed point out that the innovators who are pioneering the technology (software developers, data scientists, innovation managers, etc.) have an exceptionally large influence on digital health. They make early design decisions (which data to use, which users to serve, how the algorithm is to be coded, etc.) and will thus have a crucial influence on thousands of citizens once the technology comes into widespread use. If the innovators fail to give sufficient thought to ethical issues and moral responsibility – owing, for example, to resource considerations – this could later prove to be an obstacle to the responsible implementation of digital health.
Reason 3: Absence of appropriate regulation
The stakeholders were largely in agreement that existing regulation in the healthcare sector is inadequate. Thus legal uncertainties were frequently mentioned as a major impediment to responsible innovation. They attribute this both to the absence of new and clearly formulated rules and to the complexity of the currently applicable regulations.
The main obstacles to responsible digital health are set out in detail in the publication.
